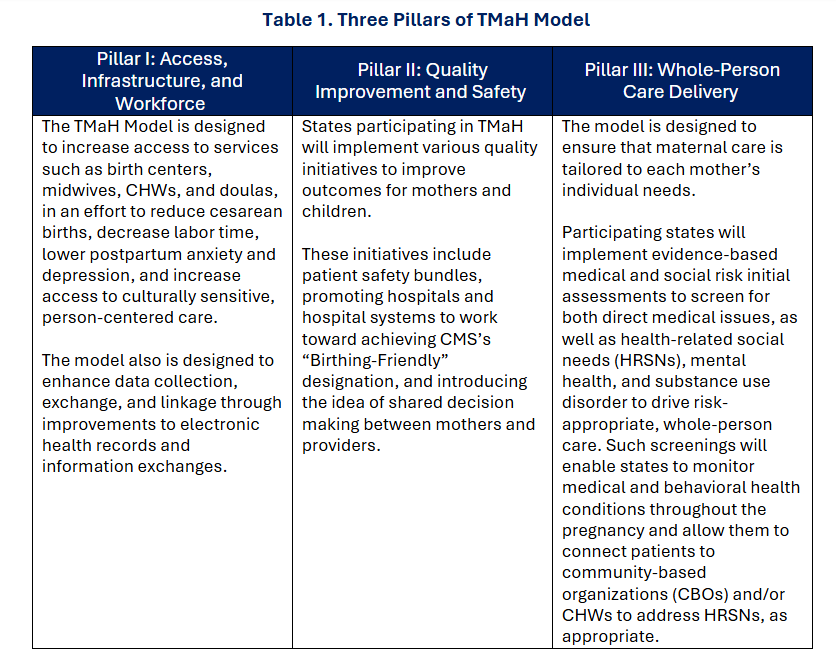
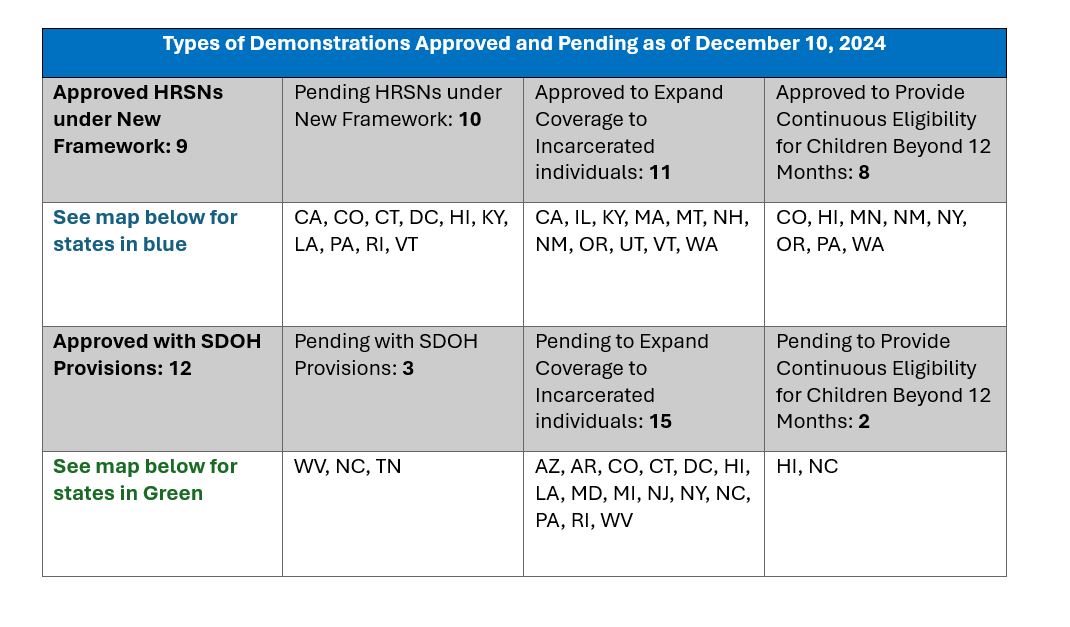
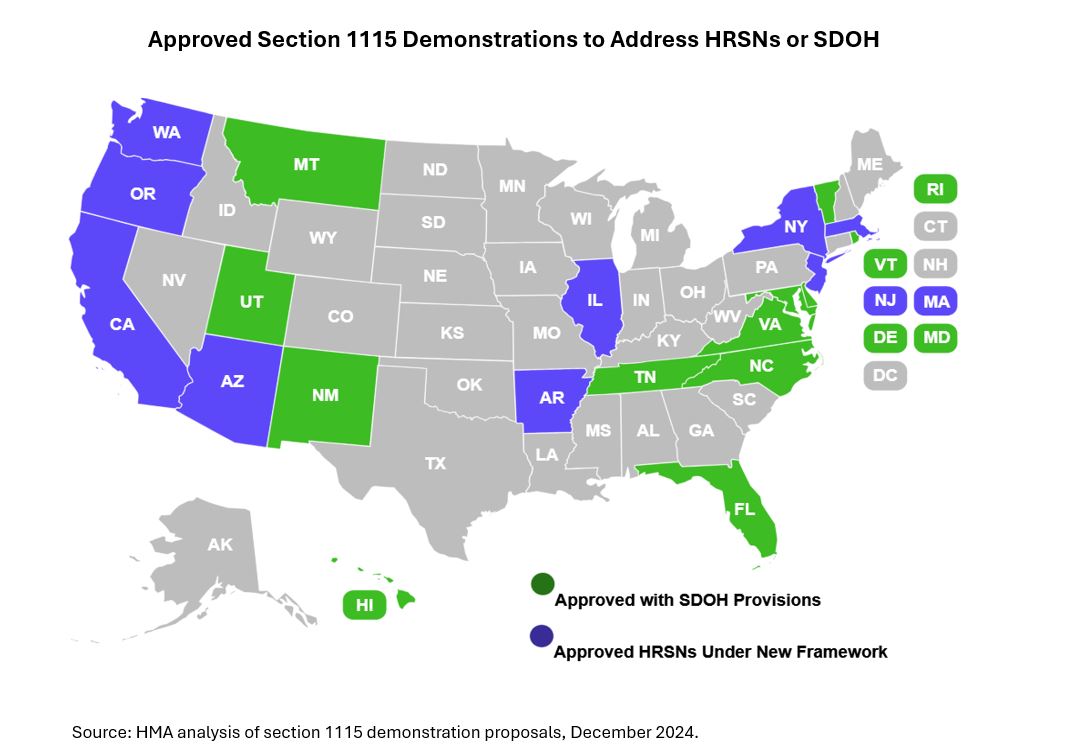
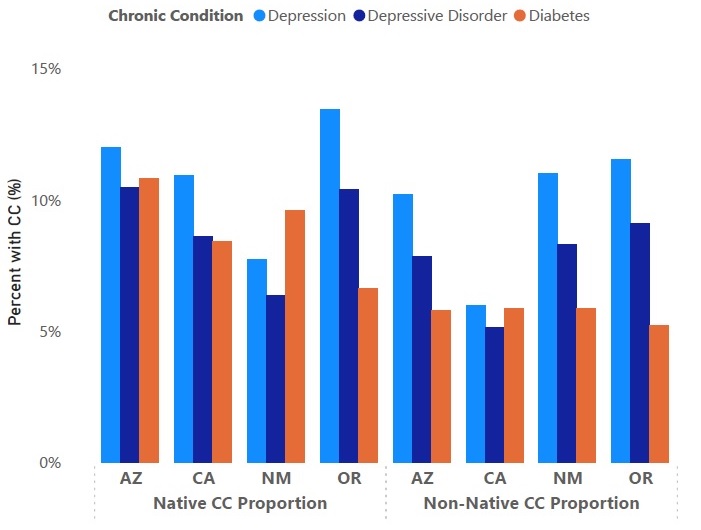
Trump Administration will Issue Final Policies
This week, our In Focus section examines the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) calendar year (CY) 2026 Advance Notice for the Medicare Advantage (MA) and Medicare Part D programs, published January 10, 2025. That same day, CMS also released draft CY 2026 Part D Redesign Program Instructions. This regulatory guidance includes CY 2026 payment updates as well as additional technical and methodological changes to MA and Part D for the coming plan year.
The release of the CY 2026 Advance Notice—along with the complementary CMS policy and technical proposed rule released in November 2024—represent the last major Medicare regulations of the Biden Administration, and these annual payment and policy updates will be finalized under the incoming Trump Administration. As a result, the proposed MA and Part D payment policies could be modified before finalization in April 2025.
Comments on the Advance Notice are due by February 10, 2025, leaving a tight timeline for MA plans and other stakeholders to provide formal feedback and written comments to CMS. Following are brief summaries of the major proposals in the Advance Notice and key considerations for stakeholders as they analyze the proposals.
Payment Impact on Medicare Advantage Organizations
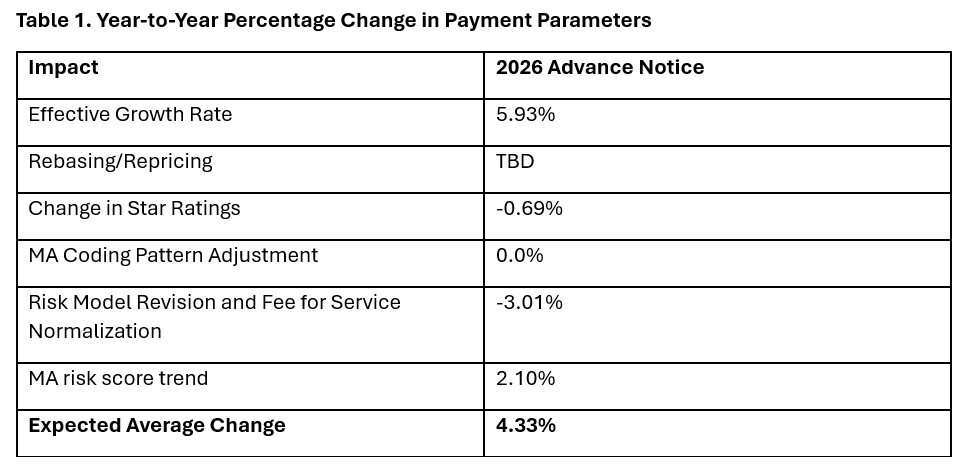
In the Advance Notice, CMS projects that federal payments to MA plans will increase by 4.33 percent from 2025 to 2026—which represents a $21 billion increase in expected payments to MA plans next year. CMS estimates that federal payments to MA plans in 2026 will total $590.9 billion.
The proposed increase in payments accounts for several factors, including growth rates in underlying costs, changes to MA Star Ratings, continued implementation of the new risk adjustment model, and MA risk score trends. The estimated growth rate considers demographic changes in MA enrollment, including projected increases in the number of enrollees.
The Advance Notice estimates represent the average increase in payments to MA plans and actual payments will vary from plan to plan. Below, Table 1 provides estimates of the impact of proposed policy changes on net MA plan payments.
MA Risk Adjustment Changes
CMS intends to complete the three-year phase-in of the MA risk adjustment model that was first published in the CY 2024 Rate Announcement. Specifically, CMS proposes to calculate 100 percent of the risk scores using the new MA risk adjustment model, referred to as the 2024 hierarchical condition categories (CMS-HCC) framework. CMS maintains that the changes to the methodology for calculating risk have improved the predictive accuracy of the model while ensuring risk-adjusted payments to MA plans are accurate.
In addition, CMS has been working to calibrate the risk adjustment model based on MA encounter data, and CMS proposes to begin phasing in an encounter-based MA risk adjustment model as soon as CY 2027.
CMS also proposes to apply the statutory minimum MA coding pattern difference adjustment factor of 5.90 percent for CY 2026.
Technical Adjustment to Cost Calculations Related to Medical Education Costs
Similar to changes in the MA risk adjustment model, CMS plans to complete the three-year phase-in of technical adjustments to the per capita cost calculations related to indirect and direct medical education costs associated with services delivered to MA beneficiaries. This technical adjustment—finalized in the CY 2024 Rate Announcement—has reduced growth rates for MA plans because of the removal of MA-related medical education costs from the benchmarks.
MA Star Ratings
CMS reiterates its continued focus on moving toward a “Universal Foundation” of measures with the goal of creating metrics that center on clinical care, patient outcomes, and improved patient experiences and are aligned across CMS programs. In addition, CMS is soliciting initial feedback on both substantive measure specification updates as well as comments on new measure concepts. CMS also is seeking stakeholder feedback on modifications to the Health Equity Index, including adding social risk factors and geography (urban or rural) to the reward factor. Any specific changes to MA Star Ratings measures, including modifications to the Health Equity Index, would occur through the formal rulemaking process.
Medicare Part D Provisions
The CY 2026 Advance Notice and the CY 2026 Draft Part D Redesign Program Instructions include several payment and benefit updates as required in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022. The CY 2026 updates include:
- The CY 2026 annual out-of-pocket cost threshold for Part D covered drugs is $2,100, which is the original out-of-pocket cap of $2,000 adjusted for the annual percentage increase in average expenditures for Part D covered drugs
- Establishment of the selected drug subsidy program
- Changes to the liability of enrollees, plan sponsors, drug manufacturers, and CMS in the standard Part D benefit design, specifically to account for the start of the Medicare Drug Price Negotiation Program in 2026
- Guidance on the successor regulation exception to the IRA’s formulary inclusion requirement for selected drugs under the Medicare Drug Price Negotiation Program
Other previously implemented IRA reforms will continue in CY 2026, including no cost sharing for Medicare beneficiaries for Part D covered drugs in the catastrophic phase, which begins after the annual out-of-pocket threshold of $2,100 is reached; a $35 monthly cap on enrollee cost sharing for insulin; no cost sharing for adult vaccines recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) Advisory Commission on Immunization Practices and covered under Part D; and the requirement for Part D plans to offer the Medicare Prescription Payment Plan to beneficiaries.
What to Expect
The CY 2026 Advance Notice includes important technical, programmatic changes and payment updates for MA and Part D plans, which will be finalized when CMS publishes the final CY 2026 Rate Announcement on or before April 7, 2025. MA plans and other stakeholders have a rigid timeframe to provide formal input and written comments to CMS before the February 10 deadline.
Like the policy and technical changes included in the MA proposed rule, the CMS Advance Notice payment updates will be finalized under the incoming Trump Administration. MA plans and other stakeholder can anticipate that the new leadership at the US Department of Health and Human Services and CMS will closely examine and take a fresh look at the proposed payment and policy changes. Though the current CMS leadership maintains that payment updates included in the Advance Notice are sufficient to support stability in MA premiums and benefits, proposed payment policies can be modified or delayed as the new leadership takes shape.
For example, officials in the Trump Administration could seek to delay the phase in of the risk adjustment changes as well as the technical adjustment regarding medical education costs, which CMS estimates would result in an additional $10.4 billion in payments to MA plans.
Connect With Us
Medicare experts at Health Management Associates, will continue to assess and analyze the policy and political landscape, which will determine the final policies included in the CY 2026 Rate Announcement. HMA experts have the depth of knowledge, experience, and subject matter expertise to assist organizations that engage in the rulemaking process and to support implementation of final policies, including policy development, tailored analysis, and modeling capabilities.
For details about the CY 2026 MA Advance Notice and its impact on MA and Part D plans, providers, and beneficiaries, contact our featured experts below.