This week’s In Focus covers key takeaways and insights from a recently released HMA report, State Approaches to Managing the Medicaid Pharmacy Benefit: Insights from a National Survey for State Fiscal Years 2023 and 2024.
The report, released in August 2024 with support from Arnold Ventures, includes survey responses from 47 states (including DC) for state fiscal years (SFYs) 2023 and 2024. The survey instrument builds on questions posed in the 2019 Medicaid Pharmacy Study of all 50 states and the District of Columbia, which HMA and the Kaiser Family Foundation conducted.
The report discusses state trends for how Medicaid pharmacy benefits are administered across the country, including planned priorities and anticipated challenges in SFY 2025 and beyond. The findings are based on information provided by the nation’s state Medicaid Directors, Medicaid Pharmacy Directors, and other Medicaid agency experts.
Pharmacy Benefit Administration
In many states, managed care delivery systems play a pivotal role in administering Medicaid benefits, including prescription drugs. As of July 1, 2023, survey results found that:
- A total of 33 states carved pharmacy benefits into managed care organization (MCO) contracts, with one state, Kentucky, directing its MCOs to use a single state-selected pharmacy benefit manager (PBM).
- Eight states carve-out the pharmacy benefit—double the number in 2019.
MCO states were surveyed about their use of carve outs for certain drug products/classes, inclusive of physician-administered drugs covered under the medical benefit.
- In all, 19 states reported carving out one or more drug classes or select agents within a drug class—often high-cost specialty drugs.
- Of those states, 13 reported using the carve-out as part of a risk mitigation strategy.
Pharmacy Benefit Managers
The significant role and market power of PBMs have prompted many state legislatures to enact greater transparency practices and require health plans to accept more responsibility for monitoring the PBMs they contract with, which reflect notable changes since the 2019 survey. More specifically:
- A total of 33 states reported contracting with a PBM.
- The most frequently reported PBM functions included utilization management, drug utilization review, claims processing and/or payment, and rebate administration activities.
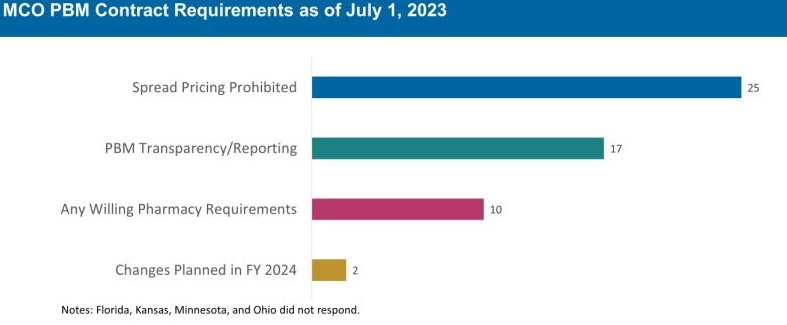
The 30 MCO states that carve in pharmacy benefits responded to survey questions about PBM transparency and spread pricing requirements. Of these states:
- 25 prohibit spread pricing in MCO PBM contracts—more than double the number of states reporting prohibitions on spread pricing in 2019.
- 17 reported having PBM transparency reporting requirements.
- 10 states reported having “any willing” pharmacy requirements.
The Role of PDLs, Prior Authorization, and Step Therapy in Controlling Drug Costs and Utilization
HMA’s experts also sought information on state payment strategies and utilization management protocols that are used to manage pharmacy expenditures. Nearly all responding states (44) have a preferred drug list (PDL) in place for fee-for-service prescriptions, which allow states to drive the use of lower cost drugs by encouraging providers to prescribe preferred drugs. Further, nearly two-thirds of responding MCO states (19 of 30 states) that do not carve out the pharmacy benefit reported having a uniform PDL for some or all drug classes, requiring all MCOs to cover the same drugs.
Many states have implemented step therapy and prior authorization (PA) guardrails in their Medicaid programs through legislation. However, 85.1 percent of responding states (40 of 47) report utilization controls like PA or step therapy applied to drugs that are reimbursed through the medical benefit to control utilization and costs. States also play an active role in managing MCO clinical protocols or medical necessity criteria, with 22 out of 30 MCO pharmacy carve-in states reporting that they require uniform clinical protocols for some or all drugs with clinical criteria. Approximately one-half of responding MCO carve-in states also require review and approval of MCOs’ PA criteria (15 of 30 states) and step therapy criteria (14 of 30 states).
State Adoption of VBAs: Improving Patient Access to Cell and Gene Therapies
A growing number of states are actively considering entering into value-based arrangements (VBAs) with manufacturers, as pressure to improve patient access to cell and gene therapies increases. Nine states have at least one VBA in place, and 23 states reported that VBAs are among their future solutions for addressing coverage of new high-cost therapies. States will need to address common barriers to VBA implementation, which involves more upfront costs and operational challenges to implement than traditional contracts.
Subsequent to the submission of survey responses, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released a Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) Access Model, which begins with a focus on sickle cell disease, anticipated to go live on January 1, 2025. Under the model, CMS will negotiate outcomes-based agreements with manufacturers on behalf of the state to ensure that treatment pricing is related to treatment effectiveness. In the coming years, experiences with this model will help determine whether a CMS-led approach to developing and administering VBAs for CGTs improves Medicaid member access to innovative treatment and their impact on expenditures, if any.
Looking Ahead
Managing the Medicaid pharmacy benefit has never been more challenging. In FY 2025 and beyond, most states will be focused on managing their Medicaid pharmacy budgets, especially the development of VBAs and other policies and strategies for managing new high-cost therapies. Other top priorities and challenges cited by multiple states include management of PBM arrangements and considering coverage of the new generation of GLP-1 anti-obesity medications. States also must react to changing drug marketplace conditions driven, in part, by federal policy changes to the Medicaid drug rebate formula and changes designed to lower Medicare drug costs. Drug manufacturer responses to these changes have implications for Medicaid state budgets, but also for state PDL management decisions and beneficiary access to needed medications.
Connect with Us
The upcoming event, Unlocking Solutions in Medicaid, Medicare, and Marketplace, hosted by HMA, will offer more opportunities to engage with report author Kathy Gifford at the pre-conference workshop Paying for Innovative Pharmaceuticals: State and Federal Trends Shaping Public Programs. Leaders from various sectors will join Kathy to discuss trends in prescription drug policies in public and commercial insurance programs.
For details about the report, contact our featured experts below.