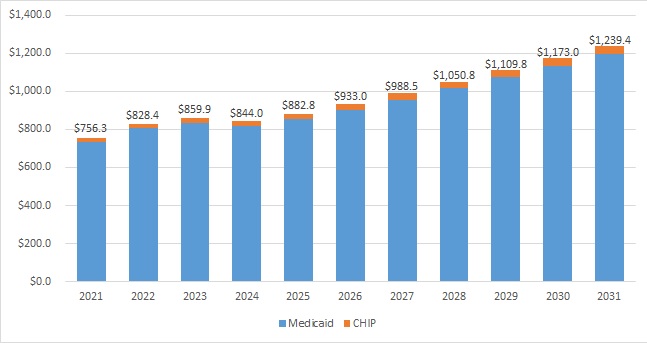
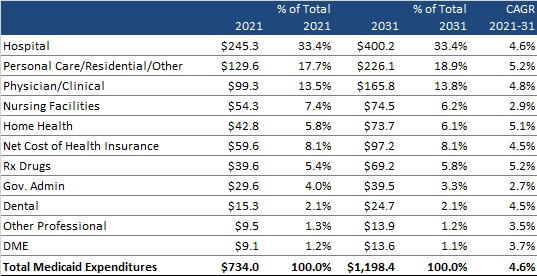
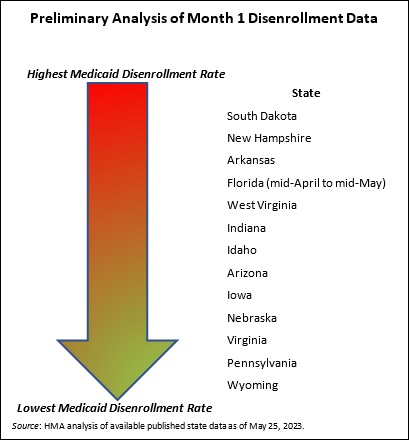
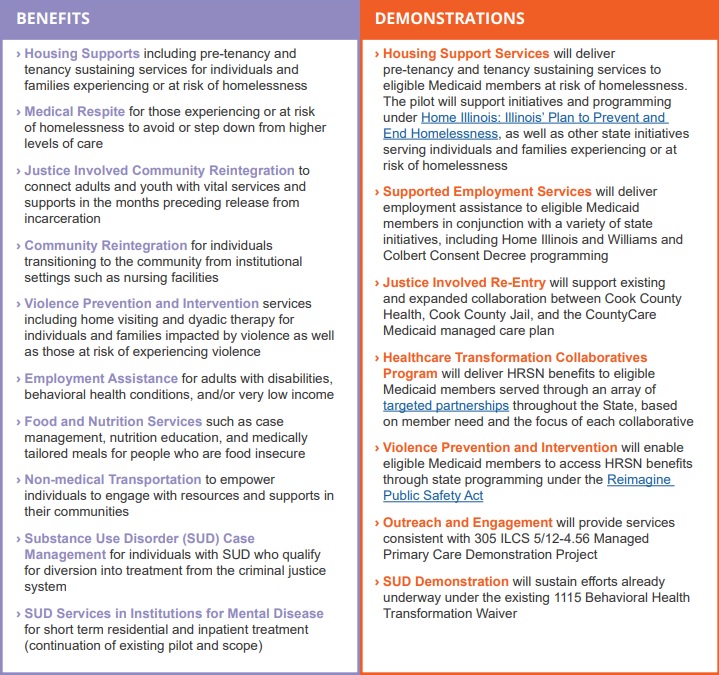
This week’s In Focus section is the first in a summer series of analysis and insights from Health Management Associates (HMA) on recent Medicare payment and policy developments. Our series kicks off with a big-picture take on the slew of regulations the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has released over the past two weeks. In future posts, we will dig deeper into several of the planned changes to highlight their potential impact on financial and operational decisions across the healthcare industry.
In July, CMS published three significant proposed Medicare rules for calendar year (CY) 2024: the Physician Fee Schedule (PFS) Proposed Rule, which includes proposed changes to the Medicare Shared Savings Program (MSSP); a proposed remedy to 340B-acquired drug payment policy for CY 2018−2022; and the Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System and Ambulatory Surgical Center Payment System (OPPS-ASC) Proposed Rule. Comments on these proposals are due to CMS in early September.
HMA’s experts note several trends across these three Medicare payment regulations:
- Health equity remains a significant focus of CMS and the Biden Administration.
- The agency is expanding its coverage of behavioral health services under Medicare and enhancing payment and access for these services.
- The long-term focus of CMS continues to be the transition toward value-based care.
- Medicare is incrementally moving toward supporting care that is delivered where and how Medicare beneficiaries prefer, for example moving away from reimbursing largely for face-to-face services and supporting reimbursement for telehealth services in more situations.
- CMS is creating pathways for reimbursement for a broader range of clinicians and caregivers who are addressing Medicare beneficiaries’ care needs.
- CMS continues its efforts to improve hospital price transparency with policies aimed at encouraging providers to publicly report data.
Medicare policy experts at HMA and is affiliate, The Moran Company, summarize details on these regulations below. These colleagues work collaboratively to monitor legislative and regulatory developments in the physician, 340B, and outpatient and ASC policy arenas and to assess the impact of changes in these reimbursement systems. HMA’s Medicare experts interpret and model policy proposals and use these analyses to assist clients in developing their strategic plans and comment on proposed regulations. Moran annually replicates the methodologies CMS uses to set payments and recommends alternative payment policies to help support its clients’ comments on various rules and to help clients understand the impact of specific policies. In addition, HMA’s other partner companies, including Wakely and Leavitt Partners, are monitoring these issues from their unique perspectives.
For more information or questions about the policies described below, please contact Amy Bassano ([email protected]), Zach Gaumer ([email protected]), Andrea Maresca ([email protected]), Kevin Kirby ([email protected]), or Rachel Kramer ([email protected]).
Medicare Physician Fee Schedule Proposed Rule (CY 2024)
The Medicare PFS establishes payments and policies for physicians and other healthcare professionals. By statute, PFS payment rates will decline by 1.25 percent from CY 2023 to 2024. However, when coupled with budget neutrality adjustments for other policy changes, the proposed PFS conversion factor will decline by 3.34 percent. The impact of this reduction will vary by physician specialty.
Behavioral Health Services: CMS implements provisions in the Consolidated Appropriations Act (CAA), 2023, which would allow Medicare coverage and payment for the services of marriage and family therapists (MFTs) and mental health counselors (MHCs). CMS proposes to classify addiction counselors who meet certain requirements as MHCs. The rule outlines how these practitioners can enroll in Medicare and bill for services starting January 1, 2024. CMS is establishing new codes and payment for psychotherapy for crisis services and proposed refinements to Health and Behavior Assessment/Intervention codes to allow additional practitioners to bill for these services and to increase the valuations of timed behavioral health services. CMS seeks comment on ways to expand access to behavioral health services. CMS specifically is looking for information on digital therapies, remote physiologic monitoring, and remote therapeutic monitoring services.
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Office Visit Services: CMS proposed to implement separate payment for an add-on billing code to account for the additional resources associated with primary care or ongoing care related to a patient’s single serious or complex chronic condition. This complexity-based add-on code may be reported with all office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M) visit level codes, and CMS estimates it will be reported for 38 percent of all O/O E/M visits initially. This estimate contributes to a significant portion of the relative value unit (RVU) budget-neutrality adjustment applied to the conversion factor. CMS also requests comments on evaluating E/M services more regularly and comprehensively including ways to improve data collection and methodologies to establish more timely improvements and accurate payments for E/M and other services.
Telehealth: CMS proposes several additions to the list of covered telehealth services and implements the various telehealth provisions included in CAA 2023, such as allowing the patient’s home to serve as an originating site. This provision would expand the scope of permitted telehealth providers and allow rural health clinics and federally qualified health centers (FQHCs) to provide telehealth services until December 31, 2024. In addition, CMS proposes opportunities for teaching physicians and medical residents to continue to use telehealth services to meet the supervision requirements via telehealth.
Caregiver Training Services: CMS proposed a new payment for practitioners who train caregivers to implement a treatment plan and support patients with diseases like dementia.
Payment for Community Health Integration, Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) Risk Assessment, and Principal Illness Navigation Provided by Social Workers, Community Health Workers, Care Navigators, and Peer Support Specialists: CMS is establishing opportunities for these services to be paid separately and account for the specific resources necessary to provide these services.
Dental Services: Although Medicare generally is prohibited from paying for dental services, CMS proposed to pay for certain dental services related to the treatment of head and neck cancers and when linked to other covered services used to treat cancer.
Discarded Drugs: The proposed rule continues the implementation process for a statutory requirement that drug and biological manufacturers refund amounts paid for discarded single-use prescription drug vials. CMS provides the list of products for which refunds would have been due in 2021, and the number of products included is expected to increase over time.
340B and Outpatient Offset Proposed Rule
In the 340B proposed rule, CMS proposed retrospective payments to 340B hospitals for incorrect payments made in CYs 2018−2022. After extensive litigation and a Supreme Court ruling, CMS will return to paying 340B hospitals for drugs using the formula of the average sales price (ASP) +6 percent, rather than the formula of the ASP −22.5 percent. In this proposed rule, CMS proposes to correct past underpayments to 340B hospitals by making lump sum payments to affected 340B hospitals. These retrospective payments are estimated to amount to $9 billion, and we anticipate payments will be made to hospitals at the beginning of CY 2024.
In addition, CMS proposed a corresponding prospectively budget neutrality offset to the 340B spending increase that will reduce hospital outpatient payments for non-drug outpatient services by 0.5 percent each year beginning in 2025. Specifically, CMS proposes to maintain this reduction until $7.8 billion in spending has been offset, which it estimates will take 16 years. The impact of this policy on the hospital industry will be significant and will create groups of winners and losers. Winners will include 340B hospitals, despite the fact that the outpatient offset will also affect their payment rates. Losers will include non-340B hospitals, particularly if their service mix is heavily focused on outpatient surgical services. Overall, the industry will observe a reduction in outpatient spending of roughly $300 million to $600 million per year for each of the 16 years the policy is in place.
Hospital Outpatient Proposed Rule (CY 2024)
Under the OPPS proposed rule, CMS would update payments for outpatient and ASC services by 2.8 percent in CY 2024 from CY 2023. This change will increase payments for hospital outpatient services by $1.9 billion and for ASC services by $170 million. In addition, if the 340B proposal is finalized, the 0.5 percent payment offset would not reduce CY 2024 OPPS payment rates but would begin reducing outpatient payments in CY 2025.
Behavioral Health: CMS proposes to establish the Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP) for behavioral health services provided to Medicare beneficiaries. The IOP proposal addresses one of the main gaps in behavioral health coverage in Medicare and promotes access to related services. CMS will define IOP as a distinct outpatient program of psychiatric services provided to individuals with acute mental illness or substance use disorder. Services could be provided at hospital outpatient departments, community mental health centers, FQHCs, and RHCs. Further, the agency proposed to establish two IOP service codes for each provider type—one for days with three services per day and another with four or more services per day.
Price Transparency: CMS proposes to increase the rigidity of its price transparency reporting program in an effort to improve hospital industry compliance with the reporting of hospital charge data to the public.
The HMA Medicare team and reimbursement experts will continue to analyze these proposal alongside other policy and reimbursement changes that affect Medicare providers. We have the depth and breadth of expertise to assist with tailored analysis, to model policy impacts, and to support clients that intend to draft comment letters on this proposed rule.